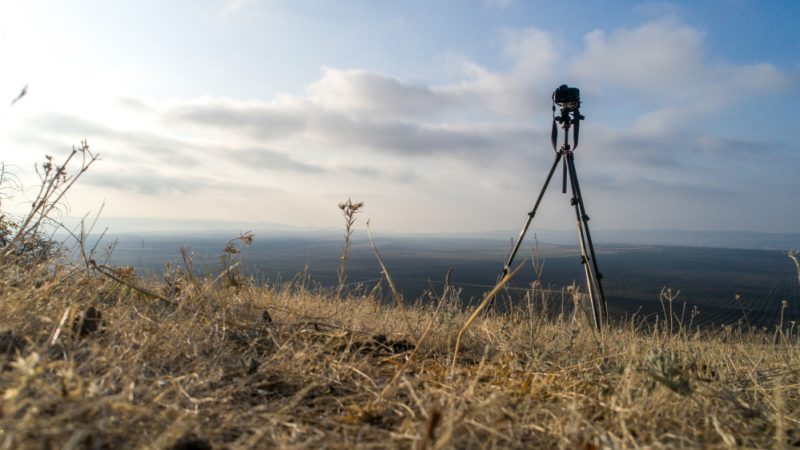
Photography has evolved beyond simple point-and-shoot devices. Today, capturing breathtaking views from miles away is possible thanks to telescopic cameras. Whether you are photographing wildlife, observing celestial bodies, or filming faraway landscapes, telescopic cameras provide exceptional magnification and clarity.
This comprehensive guide explores what telescopic cameras are, how they work, their advantages, and the best techniques for using them effectively in long-distance photography.
What Is a Telescopic Camera?
A telescopic camera is a specialized optical device designed for capturing clear images of distant objects. It combines the functions of a camera and a telescope, allowing users to zoom in far beyond the capabilities of standard lenses.
Unlike regular cameras, which rely on short focal length lenses, telescopic cameras use long focal lengths to magnify distant scenes while maintaining image sharpness and detail. They are commonly used in wildlife photography, sports events, surveillance, astronomy, and scientific observation.
The goal of a telescopic camera is simple: to make faraway subjects appear as if they are within reach, without losing quality or focus.
How Telescopic Cameras Work
The science behind a telescopic camera lies in its optical zoom system and lens configuration. The camera uses multiple lens elements to gather light and magnify distant subjects. The longer the focal length, the greater the magnification.
When light enters the lens, it is bent and focused through a series of lenses and mirrors, much like a telescope. The camera’s sensor then captures the magnified image, converting it into a high-resolution photo or video.
Modern telescopic cameras often combine optical zoom with digital enhancement to improve clarity even at extreme distances. Advanced stabilization systems also help reduce blur caused by camera shake, which becomes more noticeable at high magnifications.
Key Features of a Telescopic Camera
When looking for a quality telescopic camera, several features set them apart from standard cameras:
- Long focal length: Typically ranges from 400mm to over 2000mm, allowing extreme zoom capabilities.
- High-resolution sensors: Capture detailed images even in low light or from far away.
- Image stabilization: Reduces motion blur caused by hand movement or wind.
- Manual and automatic focus options: Enables fine control over distant subjects.
- Durable design: Often weather-resistant for outdoor or field photography.
- Video recording capability: Allows long-range filming in high definition.
Some advanced models also include Wi-Fi connectivity, GPS tagging, and AI-assisted autofocus for tracking moving subjects.
Types of Telescopic Cameras
There are different categories of telescopic cameras, each designed for specific uses. Understanding them can help you choose the right one for your needs.
a. Fixed-Lens Telescopic Cameras
These cameras have built-in zoom lenses that cannot be replaced. They are compact, easy to use, and ideal for travelers or hobbyists who want simplicity and portability.
b. Interchangeable Lens Cameras
Used mainly by professionals, these cameras allow users to swap out lenses depending on the shooting situation. Pairing a DSLR or mirrorless body with a powerful telephoto or zoom lens can provide remarkable results.
c. Smartphone Telescopic Attachments
With the rise of mobile photography, many users now attach external telescopic lenses to their smartphones. These attachments offer extended zoom capabilities and are great for casual long-distance photography.
d. Digital Telescopic Cameras
These combine optical zoom with digital enhancement, using advanced algorithms to improve clarity and sharpness even at maximum zoom levels.
Applications of Telescopic Cameras
Telescopic cameras have diverse applications across multiple fields:
- Wildlife Photography: Capture animals in their natural habitat without disturbing them.
- Astronomy: Observe celestial bodies like the moon, stars, and planets.
- Sports and Events: Zoom in on distant players or performers with precision.
- Security and Surveillance: Monitor large areas from a single vantage point.
- Marine and Landscape Photography: Capture ships, mountains, or landmarks from far distances.
The ability to shoot from afar makes telescopic cameras an essential tool for both professionals and enthusiasts who value detail and perspective.
Advantages of Using a Telescopic Camera
There are many benefits to investing in a telescopic camera for long-distance photography.
- Exceptional zoom range: The main advantage is the ability to photograph faraway objects clearly.
- Detailed imagery: High-quality optics ensure clarity and sharpness at extreme distances.
- Safety and discretion: You can observe wildlife or events from a safe distance without interference.
- Creative flexibility: Allows new perspectives and compositions impossible with standard cameras.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of photography styles and environments.
These advantages make telescopic cameras valuable not only for professionals but also for explorers, travelers, and content creators.
Common Challenges in Long-Distance Photography
While telescopic cameras offer impressive benefits, they also come with a few challenges that photographers should be aware of.
- Camera shake: High magnification makes even slight movements visible, causing blurry images.
- Atmospheric distortion: Heat waves, fog, or pollution can distort distant scenes.
- Lighting issues: Shooting long distances often requires extra light or slower shutter speeds.
- Weight and portability: Larger telescopic setups can be heavy and require tripods or stabilization gear.
These challenges can be managed with proper equipment, techniques, and post-processing tools.
Tips for Taking Stunning Long-Distance Photos
Mastering telescopic photography takes practice, but the following tips can help you achieve professional results:
- Use a tripod: Stabilization is crucial when using long lenses.
- Adjust your shutter speed: Faster shutter speeds help prevent motion blur.
- Shoot during early morning or late afternoon: The lighting is softer and atmospheric distortion is minimal.
- Use manual focus: This ensures better precision for distant subjects.
- Experiment with composition: Try different angles and focal points to create depth and interest.
For beginners, starting with a smaller zoom and gradually learning to manage longer focal lengths is the best approach.
Choosing the Right Telescopic Camera
Selecting the ideal telescopic camera depends on your goals, experience, and budget. Consider the following factors:
- Purpose: Are you photographing wildlife, sports, or the night sky? Each use may require different features.
- Focal length and zoom range: A higher zoom offers more reach but can be harder to stabilize.
- Sensor quality: A larger sensor captures more detail and performs better in low light.
- Portability: Travelers may prefer lighter, compact models, while professionals may opt for heavier but more powerful options.
- Budget: Telescopic cameras range from affordable smartphone attachments to high-end professional systems.
Reading reviews and testing different models can help you make an informed decision.
The Future of Telescopic Cameras
The future of telescopic camera technology is promising. With advancements in AI-powered stabilization, adaptive optics, and high-resolution sensors, capturing distant objects will become easier and more precise.
Manufacturers are now developing hybrid systems that combine traditional lenses with computational photography to produce even clearer images at extreme distances. Smartphone cameras are also rapidly improving, with some models offering periscope-style zoom lenses that rival professional equipment.
As technology continues to evolve, telescopic cameras will become more accessible, compact, and capable, transforming how we experience long-distance photography.
Conclusion
Telescopic cameras open a window to distant worlds, enabling photographers to capture moments and details invisible to the naked eye. Whether you are photographing wildlife across a valley, a ship on the horizon, or the surface of the moon, these powerful devices bring the faraway closer with precision and beauty.
Understanding how they work, their benefits, and their limitations allows you to make the most of your long-distance photography journey. With the right techniques and equipment, a telescopic camera can help you see and capture the world in ways that ordinary lenses never could.
FAQs
1. What makes a telescopic camera different from a regular camera?
A telescopic camera uses long focal length lenses to magnify distant objects, allowing you to photograph scenes far beyond the reach of standard lenses.
2. Can I attach a telescopic lens to my smartphone?
Yes, many smartphone-compatible telescopic lenses are available. They attach to your phone’s camera and extend its zoom range for clearer long-distance shots.
3. Do I need a tripod for a telescopic camera?
While not always required, a tripod greatly improves image stability and clarity, especially when shooting at high zoom levels.
4. Can telescopic cameras be used for night photography?
Yes. Many models perform well in low light, particularly those with larger sensors and wide-aperture lenses, making them suitable for stargazing and nighttime landscapes.
5. Are telescopic cameras suitable for beginners?
Absolutely. Entry-level models and smartphone attachments offer easy handling and automatic settings that make them accessible to beginners learning long-distance photography.
Also read: Goreweb – The Dark Side of Online Content and How to Stay Safe