Taiwan is located in one of the most seismically active regions in the world, making it prone to earthquakes. As a result, Taiwan earthquake preparedness is crucial for ensuring the safety of its citizens and minimizing damage to infrastructure. This article explores 10 key facts about Taiwan earthquake preparedness, including government policies, community efforts, and personal safety measures.
History of Taiwan Earthquake
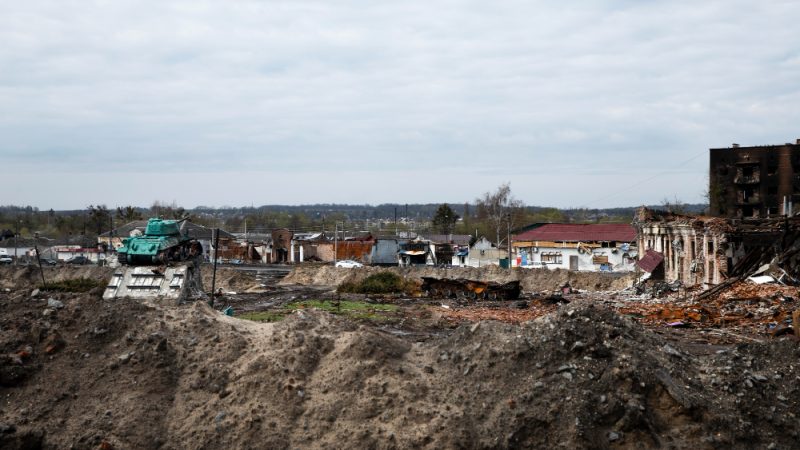
Taiwan has a long history of significant earthquakes, with some causing considerable damage and loss of life. The 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake, a magnitude 7.3 quake, is one of the most devastating in Taiwan’s history. Understanding the frequency and severity of past earthquakes is critical for planning future preparedness efforts.
The Role of Government in Preparedness
The Taiwanese government plays a central role in earthquake preparedness. Through the Central Weather Bureau and other agencies, the government monitors seismic activity and issues warnings. Building codes and safety regulations have been updated to improve resilience against earthquakes, with mandatory retrofitting for older structures.
Early Warning Systems
Taiwan earthquake early warning systems are designed to provide rapid alerts when seismic activity is detected. These systems can offer a few seconds to minutes of warning, allowing people to take cover or halt critical operations. Taiwan’s early warning system uses a network of sensors to detect ground movement and trigger alerts through mobile devices and public broadcast systems.
Community Earthquake Drills
Community drills are an essential part of Taiwan earthquake preparedness. These drills, often organized by local governments and schools, teach people how to respond during an earthquake. They cover essential safety practices, such as “Drop, Cover, and Hold On,” and help ensure that everyone knows evacuation routes and assembly points.
Personal Emergency Kits
Personal emergency kits are a key component of Taiwan earthquake preparedness. These kits contain essential items like water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, flashlights, and batteries. The government and non-profits often provide guidelines on assembling a proper emergency kit to ensure individuals are prepared for the first 72 hours after an earthquake.
Structural Reinforcement and Building Codes
Taiwan’s building codes have evolved to address the risk of earthquakes. Modern buildings must meet strict seismic design requirements, and older buildings are subject to retrofitting to improve their earthquake resistance. Structural reinforcement is crucial to minimize damage and prevent collapse during a Taiwan earthquake.
Public Education and Awareness Campaigns
Public education and awareness campaigns play a significant role in Taiwan earthquake preparedness. The government, along with non-profit organizations, regularly conducts educational programs to inform the public about earthquake risks and safety measures. These campaigns include TV ads, brochures, and interactive workshops.
Earthquake-Proofing Homes and Businesses
Home and business owners in Taiwan are encouraged to earthquake-proof their properties. This involves securing heavy furniture, reinforcing walls, and installing safety latches on cabinets. Earthquake-proofing reduces the risk of injury from falling objects and helps prevent damage to personal property during a Taiwan earthquake.
Coordination with International Organizations
Taiwan coordinates with international organizations to improve earthquake preparedness. By collaborating with seismic research institutions and disaster response agencies, Taiwan gains access to the latest technologies and best practices. This coordination also facilitates international aid and support in the event of a major Taiwan earthquake.
Role of Volunteers and NGOs
Volunteers and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are instrumental in Taiwan earthquake preparedness and response. These groups help with community education, emergency response, and post-earthquake recovery efforts. Their work ensures that vulnerable populations receive the assistance they need and that communities are better prepared for future earthquakes.
Conclusion
Preparedness is key to mitigating the impact of a Taiwan earthquake. By understanding the unique seismic risks of the region and taking proactive measures, Taiwan can reduce casualties and damage during a quake. The efforts outlined in these 10 key facts—from government regulations to community drills—contribute to a safer environment for everyone in Taiwan.
FAQs
1. How often do earthquakes occur in Taiwan?
Earthquakes are common in Taiwan due to its location on the boundary of the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Minor tremors occur frequently, while major earthquakes happen less often but can cause significant damage.
2. What should I do during a Taiwan earthquake?
During a Taiwan earthquake, follow the “Drop, Cover, and Hold On” protocol. Find a safe spot away from windows and heavy objects, cover your head and neck, and hold on to something stable. After the shaking stops, evacuate if necessary and follow local emergency instructions.
3. How does Taiwan’s early warning system work?
Taiwan’s early warning system uses a network of sensors to detect seismic activity. When ground movement is detected, the system sends alerts through mobile devices, public broadcast systems, and other communication channels. The system provides a few seconds to minutes of warning before a major quake hits.
4. What should I include in a personal emergency kit for earthquakes?
A personal emergency kit should contain water, non-perishable food, first-aid supplies, flashlights, batteries, a multi-tool, and personal identification. The kit should also include items specific to your needs, such as prescription medications and infant care products if applicable.
Q5. How does Taiwan reinforce its buildings for earthquake resistance?
Taiwan has strict building codes that require modern structures to be designed with seismic resistance in mind. Older buildings are subject to retrofitting to improve their earthquake resistance. Reinforcements include additional steel framing, shear walls, and base isolators to minimize damage during an earthquake.
Also read: FORKLIFT TRUCK IS USED FOR: 10 ESSENTIAL APPLICATIONS IN WAREHOUSES