The Sony/Philips Digital Interface, commonly known as S/PDIF, is a digital audio format designed to transmit high-quality sound signals between devices. Developed by Sony and Philips, S/PDIF is a key component in home audio systems, professional studios, and digital entertainment setups. Its ability to carry uncompressed audio ensures superior sound quality, making it a favorite among audiophiles and audio engineers alike.
In this article, we’ll dive into what S/PDIF is, how it works, its advantages, and how to use it in your audio setup for optimal performance.
What Is S/PDIF?
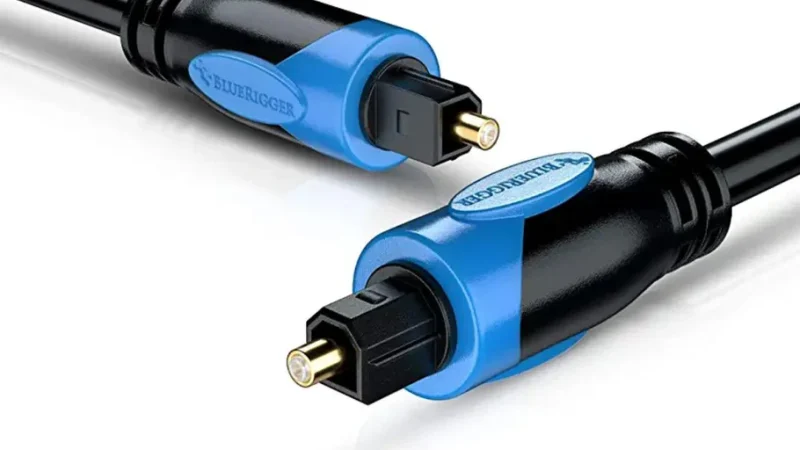
The Sony/Philips Digital Interface (S/PDIF) is a standard for transmitting digital audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect audio sources, such as TVs, Blu-ray players, or gaming consoles, to external devices like soundbars, receivers, or DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters).
Key Features:
- Digital Audio Transmission: Transmits high-quality, uncompressed digital audio.
- Two Formats: Available in optical (TOSLINK) and coaxial cable formats.
- Compatibility: Widely supported by audio devices, from consumer electronics to professional equipment.
- Surround Sound Support: Capable of carrying surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS.
How Does S/PDIF Work?
S/PDIF transmits audio signals in a digital format, using either electrical pulses (via coaxial cables) or light signals (via optical cables). The format ensures minimal signal degradation, resulting in crystal-clear audio quality.
Steps in Audio Transmission:
- Source Device: Generates digital audio signals (e.g., TV, gaming console).
- S/PDIF Output: Sends the signal through an optical or coaxial connection.
- Receiving Device: Decodes the digital signal into audio for playback (e.g., soundbars, amplifiers).
S/PDIF Formats: Optical vs. Coaxial
S/PDIF is available in two formats: optical and coaxial. Each has its unique features and advantages.
| Feature | Optical (TOSLINK) | Coaxial |
| Signal Transmission | Light signals through fiber-optic cables. | Electrical pulses through copper cables. |
| Durability | Immune to electrical interference. | May be affected by electromagnetic noise. |
| Cable Type | Fiber-optic, fragile but lightweight. | Copper, more durable but slightly bulkier. |
| Max Cable Length | Typically up to 10 meters. | Typically up to 15 meters. |
| Audio Quality | High, with minimal signal degradation. | High, but may be slightly more robust for longer runs. |
Benefits of S/PDIF
High-Quality Audio Transmission
S/PDIF preserves audio fidelity by transmitting digital signals, ensuring clean, uncompressed sound quality.
Universal Compatibility
Widely supported across a range of devices, including TVs, receivers, soundbars, and audio interfaces.
Support for Surround Sound
S/PDIF can transmit multi-channel audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, ideal for home theater setups.
Minimal Signal Loss
Unlike analog connections, S/PDIF reduces signal loss and interference, particularly when using optical cables.
Ease of Use
Simple plug-and-play functionality makes it easy to connect compatible devices.
Common Uses of S/PDIF
Home Theater Systems
Connect Blu-ray players, TVs, or gaming consoles to AV receivers or soundbars for high-quality audio.
Studio Equipment
Used in professional audio interfaces to transmit digital sound between devices without signal degradation.
Music Production
Allows seamless integration of DACs and amplifiers with recording equipment.
Gaming
Connects gaming consoles to external audio systems for an immersive surround sound experience.
Limitations of S/PDIF
While S/PDIF is a reliable audio format, it has some limitations:
- Bandwidth Limitations: Cannot support advanced audio formats like Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD Master Audio, which require HDMI connections.
- No Video Support: Transmits only audio signals, so it cannot carry video data like HDMI.
- Cable Length Restrictions: Limited cable lengths may not suit all setups, especially in large rooms.
- Device Dependency: Requires devices with S/PDIF ports, which may not be available on all modern equipment.
How to Use S/PDIF in Your Audio Setup
Check Compatibility
Ensure both your source and receiving devices have S/PDIF ports (optical or coaxial).
Choose the Right Cable
Decide between optical or coaxial cables based on your setup and preference.
Connect the Devices
- Plug one end of the cable into the S/PDIF output on the source device.
- Connect the other end to the S/PDIF input on the receiver or sound system.
Configure Audio Settings
Adjust the audio output settings on your source device to ensure digital sound is sent through the S/PDIF connection.
Alternatives to S/PDIF
If S/PDIF doesn’t meet your needs, consider these alternatives:
- HDMI: Supports both audio and video signals, as well as advanced audio formats.
- Bluetooth: Wireless audio transmission for modern devices, though with potential latency issues.
- USB Audio: High-quality digital audio transmission, particularly in professional setups.
Conclusion
The Sony/Philips Digital Interface (S/PDIF) is a versatile and reliable solution for high-quality audio transmission. Whether you’re setting up a home theater, producing music, or upgrading your gaming audio, S/PDIF ensures excellent sound quality with minimal interference.
Understanding its formats, benefits, and limitations allows you to make informed decisions about integrating S/PDIF into your audio system. Choose the right cable, configure your devices, and enjoy crystal-clear sound for an immersive audio experience.
FAQs
1. What is S/PDIF used for?
S/PDIF is used to transmit digital audio signals between devices like TVs, receivers, soundbars, and audio interfaces.
2. What’s the difference between optical and coaxial S/PDIF?
Optical uses light signals and is immune to electrical interference, while coaxial uses electrical pulses and is more robust over longer distances.
3. Can S/PDIF transmit surround sound?
Yes, S/PDIF supports surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, but not advanced formats like Dolby TrueHD.
4. Is S/PDIF better than HDMI for audio?
S/PDIF is excellent for audio-only setups, but HDMI is better for transmitting both audio and video and supports more advanced audio formats.
5. How long can an S/PDIF cable be?
Optical cables typically work up to 10 meters, while coaxial cables can extend up to 15 meters without significant signal loss.
Also read: Short Against the Box: Definition, Benefits, and Key Considerations