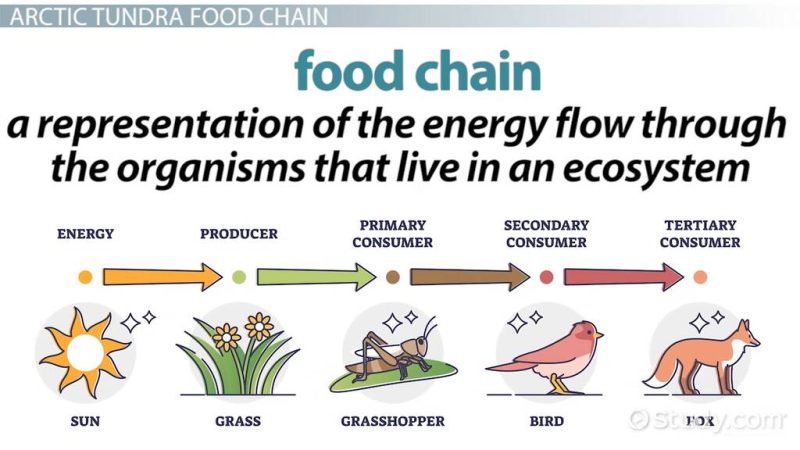
The Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web is a fascinating and delicate ecological system that supports life in one of the harshest environments on Earth. Despite the frigid temperatures, limited sunlight, and permafrost soil, a variety of plants, herbivores, and predators have adapted to survive. Wildflowers play a crucial role in this ecosystem, sustaining insects, small mammals, and even large predators through a complex web of interdependence.
In this article, we’ll explore 10 powerful secrets that allow the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web to function and thrive. From nutrient cycles to predator-prey relationships, each element contributes to maintaining the fragile balance of life in the tundra.
Wildflowers Are the Foundation of the Ecosystem
At the heart of the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web are resilient plants like Arctic poppies, purple saxifrages, and woolly lousewort. These wildflowers not only provide nectar for pollinators but also serve as a primary food source for herbivores such as lemmings and Arctic hares. Their deep root systems help anchor the permafrost, preventing erosion while absorbing vital nutrients.
The Role of Pollinators in Survival
Insects like Arctic bumblebees and hoverflies play a crucial role in the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web by pollinating wildflowers. With a short growing season, these pollinators must work efficiently to transfer pollen between flowers, ensuring successful reproduction. Without them, plant populations would decline, disrupting the entire food web.
Herbivores Keep the Balance
Small herbivores such as lemmings, voles, and Arctic hares feed on wildflowers, mosses, and lichens. Their grazing behavior helps regulate plant populations, preventing overgrowth. However, their populations fluctuate drastically due to predation and climate shifts, influencing the entire Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web.
The Impact of Large Mammals
Caribou, one of the tundra’s largest herbivores, depend on lichen, moss, and flowering plants for sustenance. In turn, they serve as prey for Arctic wolves, which play a crucial role in controlling herbivore populations. The balance between large mammals and plant life is essential for maintaining the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web.
Apex Predators Regulate the System
Predators such as Arctic foxes, wolves, and snowy owls are key to the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web. They keep herbivore populations in check, preventing overgrazing of wildflowers and other plant life. Without these top predators, herbivores could overpopulate, leading to ecosystem collapse.
Microorganisms Drive Nutrient Cycling
Beneath the tundra’s surface, microorganisms such as fungi and bacteria break down organic matter, recycling nutrients into the soil. This process enriches the permafrost, allowing wildflowers to absorb vital minerals and grow despite extreme conditions. Without these microscopic decomposers, the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web would lack essential nutrients.
Seasonal Changes Shape the Food Web
The Arctic tundra experiences drastic seasonal shifts, affecting plant growth and animal behavior. During the summer, wildflowers bloom rapidly, providing food and shelter for various species. In winter, many animals enter hibernation or migrate south, while predators rely on stored food sources. These seasonal cycles are vital to the stability of the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web.
Climate Change Poses a Major Threat
Rising temperatures and melting permafrost are disrupting the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web. Many wildflowers struggle to adapt to changing conditions, leading to reduced food sources for herbivores and, in turn, predators. As a result, species that rely on the tundra ecosystem face population declines and increased competition for resources.
Symbiotic Relationships Aid Survival
Certain species within the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web have evolved symbiotic relationships to enhance survival. For example, lichens—a fusion of fungi and algae—provide nourishment for caribou during winter. Additionally, some flowering plants form mutualistic bonds with fungi, improving nutrient absorption in harsh soil conditions. These interdependent relationships are crucial to the tundra’s ecosystem.
Human Impact and Conservation Efforts
Human activity, including industrial development, oil drilling, and climate change, threatens the delicate Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web. However, conservation efforts, such as protected wildlife reserves and sustainable environmental policies, aim to preserve this fragile ecosystem. Reducing carbon emissions and promoting responsible land use can help maintain the tundra’s biodiversity.
Conclusion
The Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web is a remarkable example of resilience in one of the planet’s harshest environments. From wildflowers supporting pollinators to predators regulating herbivore populations, every element plays a vital role in maintaining balance. However, climate change and human interference threaten this delicate ecosystem. By understanding these 10 powerful secrets, we can appreciate the importance of conservation efforts to protect the tundra’s unique biodiversity.
FAQs
Q1. Why are wildflowers important to the Arctic tundra food web?
Wildflowers serve as the base of the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web, providing food and habitat for pollinators, herbivores, and other wildlife.
Q2. How do Arctic animals survive extreme conditions?
Many Arctic animals have thick fur, hibernate, or migrate seasonally to cope with freezing temperatures and limited food availability.
Q3. What are the biggest threats to the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web?
Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are major threats that disrupt plant and animal populations in the tundra.
Q4. How do predators affect the Arctic Wild Flower Tundra Food Web?
Predators help regulate herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining ecological balance.
Q5. Can the Arctic tundra recover from environmental damage?
With conservation efforts and reduced human impact, the tundra can slowly recover, but some changes, like permafrost melting, may be irreversible.
Also read: Quick Mobile Repair Scottsdale: Fast & Reliable Device Fixes