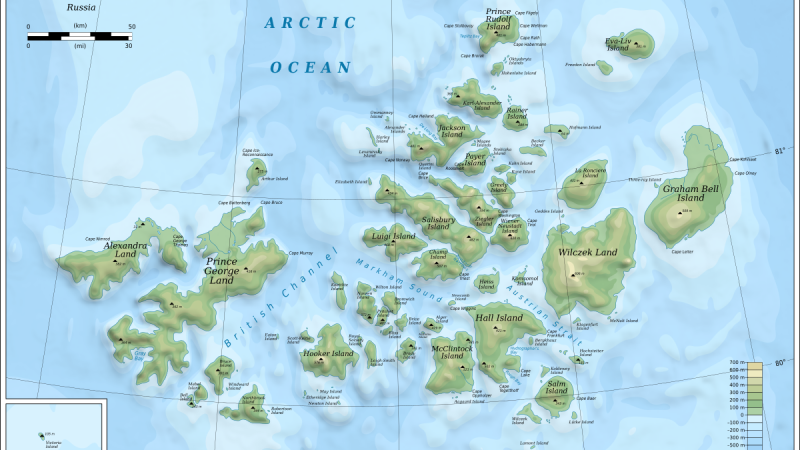
Franz Josef Island is one of the most remote and intriguing destinations in the Arctic. Located in the northernmost reaches of Russia, this archipelago boasts a unique blend of natural beauty, historical significance, and biodiversity. With its ice-covered landscapes and fascinating wildlife, Island captures the imagination of adventurers and researchers alike. Let’s dive into 10 astonishing facts about this Arctic gem that you probably didn’t know!
Franz Josef Island: The Archipelago Consists of 192 Islands
Franz Josef Island is not a single island but an archipelago made up of 192 smaller islands. These islands are spread across the Arctic Ocean and cover an area of approximately 16,000 square kilometers. Despite its vastness, much of the region is uninhabitable due to extreme weather conditions, with glaciers covering 85% of the territory.
The islands were discovered in 1873 by the Austro-Hungarian North Pole expedition. They named the archipelago after Emperor Franz Joseph I. Today, the islands remain a testament to the challenges and rewards of Arctic exploration.
One of the Northernmost Points on Earth
Franz Josef Island lies just 900 kilometers from the North Pole, making it one of the northernmost landmasses on the planet. This location subjects the islands to six months of polar night followed by six months of daylight. During the summer months, the midnight sun bathes the ice-covered landscape in an ethereal glow.
Its proximity to the North Pole also makes Island a critical area for scientific research, particularly in understanding climate change and polar ecosystems.
A Haven for Arctic Wildlife
Franz Josef Island is a sanctuary for a diverse range of Arctic wildlife. Polar bears are perhaps the most iconic residents, often seen traversing the icy terrain. Other notable species include walruses, Arctic foxes, and seals. The surrounding waters are home to whales, such as belugas and narwhals.
The islands also serve as an important breeding ground for seabirds, including guillemots and kittiwakes. The abundance of wildlife makes Island a critical habitat in the Arctic region.
Home to Stunning Glaciers
The glaciers on Franz Josef Island are among its most striking features. Covering the majority of the archipelago, these massive ice formations play a vital role in regulating the Arctic climate. Some glaciers extend all the way to the ocean, forming breathtaking ice cliffs.
Researchers frequently study these glaciers to monitor melting rates and understand their impact on global sea levels. The beauty and scientific importance of these glaciers are undeniable.
Steeped in Exploration History
Franz Josef Island has a storied history of Arctic exploration. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it became a focal point for expeditions seeking to reach the North Pole. Many of these journeys were fraught with peril, as explorers braved treacherous ice floes and extreme cold.
One of the most famous expeditions was led by Fridtjof Nansen, who used the archipelago as a base during his 1895 attempt to reach the North Pole. These stories of bravery and endurance continue to inspire adventurers today.
A Harsh Yet Beautiful Climate
The climate of Franz Josef Island is characterized by long, freezing winters and short, cool summers. Temperatures can plummet to -40°C in winter, while summer highs rarely exceed 2°C. Despite the harsh conditions, the landscape is stunning, with icebergs, snow-covered peaks, and pristine fjords creating a surreal Arctic panorama.
For visitors and researchers, the unpredictable weather adds to the adventure, emphasizing the remote and untamed nature of this Arctic wonder.
A Vital Climate Change Research Hub
Franz Josef Island plays a crucial role in the study of climate change. Its glaciers and ice caps serve as valuable indicators of global warming, with scientists monitoring their retreat over time. Additionally, the archipelago’s unique ecosystems provide insight into how climate change impacts Arctic biodiversity.
The findings from research conducted on Island contribute to global efforts to understand and combat climate change.
It Was Once a Military Outpost
During the Cold War, Franz Josef Island had a strategic military significance. The Soviet Union established bases on the archipelago, taking advantage of its remote location and proximity to NATO territories. These bases were used for air defense and monitoring purposes.
While the military presence has diminished, remnants of these installations can still be found, offering a glimpse into the region’s geopolitical history.
Accessible Only by Specialized Expeditions
Due to its remote location and extreme conditions, Franz Josef Island is accessible only by specialized Arctic expeditions. Most visitors arrive via icebreaker ships or helicopters during the brief summer months. These expeditions often focus on wildlife observation, glacier exploration, and historical landmarks.
For adventurous travelers, a journey to Island offers a once-in-a-lifetime experience, combining natural beauty with the thrill of remote exploration.
Part of Russia’s Protected Natural Areas
Franz Josef Island is part of the Russian Arctic National Park, one of the largest protected areas in the country. This designation helps preserve the unique ecosystems and wildlife of the archipelago. Strict regulations are in place to minimize human impact, ensuring that the fragile Arctic environment remains intact for future generations.
This status as a protected area underscores the global importance of Island in conserving Arctic biodiversity.
Conclusion
Franz Josef Island is more than just a remote Arctic destination—it’s a place of unparalleled natural beauty, rich history, and scientific significance. From its breathtaking glaciers to its vibrant wildlife, the archipelago offers a glimpse into a world that remains largely untouched by human activity. Whether you’re an adventurer, a history enthusiast, or a climate researcher, Island holds something truly unique.
FAQs
Q1. Where is this Arctic archipelago located?
It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, north of Russia, near the North Pole.
Q2. How can you visit this remote destination?
Access is possible through specialized expeditions, usually via icebreaker ships or helicopters during the short Arctic summer.
Q3. What types of wildlife inhabit this region?
The area is home to polar bears, Arctic foxes, walruses, seals, and a variety of seabirds. Whales such as belugas and narwhals also frequent the surrounding waters.
Q4. Why is this region significant for climate research?
Its glaciers and ecosystems provide critical insights into the effects of global warming, helping scientists monitor changes in the Arctic environment.
Q5. Who discovered this area, and when?
The archipelago was discovered in 1873 by an Austro-Hungarian expedition led by Julius von Payer and Karl Weyprecht.
Also read: Why Would You Visit the Tundra? 10 Incredible Reasons to Explore This Icy Wonderland