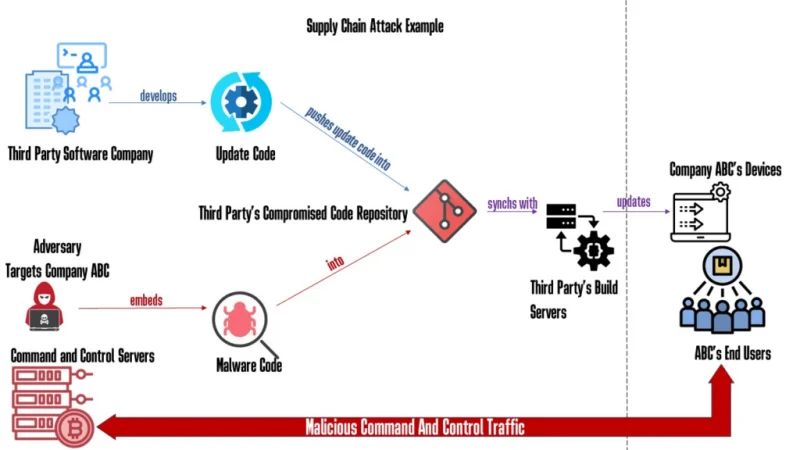
In today’s interconnected world, supply chains are critical to the smooth functioning of businesses and economies. However, they are increasingly targeted by adversarial threats—deliberate actions by malicious actors aimed at disrupting, compromising, or manipulating the supply chain. These threats can range from cyberattacks and counterfeit products to espionage and physical sabotage, posing significant risks to operations, finances, and reputations.
Understanding adversarial threats is crucial for businesses to safeguard their supply chain processes and ensure resilience against potential disruptions. This article explores the nature of these threats, their impact, and strategies for mitigation.
What Are Adversarial Threats to a Supply Chain?
Adversarial threats to a supply chain refer to deliberate actions taken by malicious actors to disrupt, manipulate, or compromise the supply chain process. These threats can arise from competitors, cybercriminals, state-sponsored actors, or insiders, targeting various vulnerabilities within a supply chain.
Such threats can have significant consequences, including financial loss, operational delays, reputational damage, and national security risks.
Common Adversarial Threats to Supply Chains
Cybersecurity Attacks
Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems to steal sensitive data, disrupt operations, or demand ransom.
Examples:
- Ransomware Attacks: Locking systems until a ransom is paid.
- Data Breaches: Stealing proprietary or customer information.
Case Study:
The Colonial Pipeline cyberattack in 2021 disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S., showcasing how vulnerable supply chains are to cyber threats.
Counterfeit and Fraudulent Products
Adversaries may infiltrate supply chains with counterfeit or substandard goods, risking product integrity and consumer safety.
Impact:
- Financial losses for companies.
- Harm to brand reputation.
Physical Disruptions and Sabotage
Malicious actors can physically damage infrastructure, equipment, or goods, causing delays and increased costs.
Examples:
- Sabotaging transport vehicles.
- Damaging warehouses or production facilities.
Espionage and Information Leaks
Competitors or hostile entities may use espionage to gain access to proprietary supply chain information, such as trade secrets or vendor contracts.
State-Sponsored Threats
Geopolitical tensions can lead to state-sponsored attacks on supply chains, particularly in critical industries like technology or healthcare.
Example:
The global semiconductor shortage revealed vulnerabilities in supply chains susceptible to geopolitical adversarial actions.
Why Are Supply Chains Vulnerable?
- Globalization: Complex international networks increase exposure to threats.
- Digital Dependency: Reliance on technology creates opportunities for cyberattacks.
- Lack of Visibility: Many companies struggle to monitor every tier of their supply chain.
- Insider Threats: Employees or partners with malicious intent can exploit internal access.
Strategies to Mitigate Adversarial Threats
Strengthen Cybersecurity
- Use encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Regularly update software and monitor for vulnerabilities.
- Conduct employee training on phishing and cyber threats.
Enhance Supply Chain Visibility
Implement tools like blockchain and IoT to track goods and ensure transparency at every stage.
Diversify Suppliers
Avoid over-reliance on a single supplier or region to reduce the impact of disruptions.
Screen Partners and Vendors
Conduct thorough due diligence on all partners to ensure they meet security and ethical standards.
Develop a Crisis Response Plan
Prepare for potential threats with a robust plan that includes incident response teams and recovery strategies.
Conclusion
Adversarial threats to supply chains pose significant risks to businesses and industries worldwide. From cybersecurity breaches to counterfeit goods, these challenges require proactive measures to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure resilience. By adopting strategies like enhanced cybersecurity, supply chain visibility, and diversified suppliers, organizations can safeguard their operations against malicious disruptions.
Protecting supply chains is not just about avoiding loss—it’s about maintaining trust and continuity in an interconnected global economy.
FAQs
1.What are adversarial threats to supply chains?
Adversarial threats involve deliberate disruptions or attacks on supply chains, such as cyberattacks, sabotage, or counterfeit goods.
2.How do cyberattacks affect supply chains?
Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, and compromise digital systems essential to supply chain management.
3.What industries are most vulnerable to supply chain threats?
Critical industries like technology, healthcare, and logistics are highly vulnerable due to their global dependencies and digital reliance.
4.How can businesses mitigate supply chain threats?
Implement robust cybersecurity measures, enhance visibility, diversify suppliers, and conduct regular risk assessments.
5.Why is supply chain security important?
Secure supply chains protect businesses from financial loss, operational delays, and reputational damage while ensuring reliable delivery of goods and services.
Also read: Vendors Lien: What It Is and How It Works